| Issue |
E3S Web Conf.
Volume 269, 2021
2021 International Conference on Environmental Engineering, Agricultural Pollution and Hydraulical Studies (EEAPHS 2021)
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Article Number | 01003 | |
| Number of page(s) | 7 | |
| Section | Environmental Engineering | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/e3sconf/202126901003 | |
| Published online | 09 June 2021 | |
Experimental study on the effects of used HEPA filters on water environment
1
Guangxi Key Laboratory of Environmental Pollution Control Theory and Technology, Guilin University of Technology, Guilin 541004, China
2
Collaborative Innovation Center for Water Pollution Control and Water Safety in Karst Area, Guilin University of Technology, Guilin 541004, China
3
College of Earth Science, Guilin University of Technology, Guilin 541004, China
* Corresponding author: shanhuimei@glut.edu.cn
In this paper, the commonly used High Efficiency Particulate Air filter (HEPA) material as the research object, through the design of indoor experiment, using pure water, groundwater, and rainwater solution to soak, analysis of unused and abandoned the mesh in different water chemical solution release/adsorption law of anion and metal components, in order to find out its potential impact on the water environment. Results showed that: (1) when the waste HEPA filters were soaked in water solutions, the maximum average release amounts $$(\overline {{Q_{max}}} )$$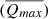 of four anions were in a order as: $${\rm{SO}}_4^{2 - } > {\rm{NO}}_3^ - > {\rm{C}}{{\rm{l}}^ - } > {{\rm{F}}^ - }$$
of four anions were in a order as: $${\rm{SO}}_4^{2 - } > {\rm{NO}}_3^ - > {\rm{C}}{{\rm{l}}^ - } > {{\rm{F}}^ - }$$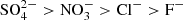 . Pure waters showed the highest $$(\overline {{Q_{max}}} )$$
. Pure waters showed the highest $$(\overline {{Q_{max}}} )$$ of Cl- and $${\rm{NO}}_3^ - $$
of Cl- and $${\rm{NO}}_3^ - $$ , which were 1.2120 and 0.3387 mg/g, respectively. Groundwater showed the highest $$(\overline {{Q_{max}}} )$$
, which were 1.2120 and 0.3387 mg/g, respectively. Groundwater showed the highest $$(\overline {{Q_{max}}} )$$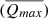 of $${\rm{SO}}_4^{2 - } > $$
of $${\rm{SO}}_4^{2 - } > $$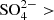 and F-, which were 6.7329 and 0.0348 mg/g. These indicated that $${\rm{SO}}_4^{2 - } > $$
and F-, which were 6.7329 and 0.0348 mg/g. These indicated that $${\rm{SO}}_4^{2 - } > $$ was the major anion pollutant for waste HEPA filters soaked in water solutions, and groundwater and pure water were more susceptible to be contaminated by anions released from waste HEPA filters. (2) the $$(\overline {{Q_{max}}} )$$
was the major anion pollutant for waste HEPA filters soaked in water solutions, and groundwater and pure water were more susceptible to be contaminated by anions released from waste HEPA filters. (2) the $$(\overline {{Q_{max}}} )$$ of three metals released from waste HEPA filters were in a order as Zn> Pb> As, in which, groundwater showed the highest $$(\overline {{Q_{max}}} )$$
of three metals released from waste HEPA filters were in a order as Zn> Pb> As, in which, groundwater showed the highest $$(\overline {{Q_{max}}} )$$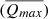 of Zn (2.21 μg/g), followed by rainwater and pure water. This meant that Zn is the major heavy metal pollutant released from waste HEPA filters into the water environment, and groundwater was more susceptible to be contaminated by metals released from waste HEPA filters. (3) None Zn, Pb, and As were released in these three different solutions for the unused filter, indicating that it has almost no contamination threat to the water environment. This study is expected to further improve the understanding of water environmental pollution prevention and management, and provide a theoretical basis for China’s ecological environment protection.
of Zn (2.21 μg/g), followed by rainwater and pure water. This meant that Zn is the major heavy metal pollutant released from waste HEPA filters into the water environment, and groundwater was more susceptible to be contaminated by metals released from waste HEPA filters. (3) None Zn, Pb, and As were released in these three different solutions for the unused filter, indicating that it has almost no contamination threat to the water environment. This study is expected to further improve the understanding of water environmental pollution prevention and management, and provide a theoretical basis for China’s ecological environment protection.
© The Authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2021
 This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.



